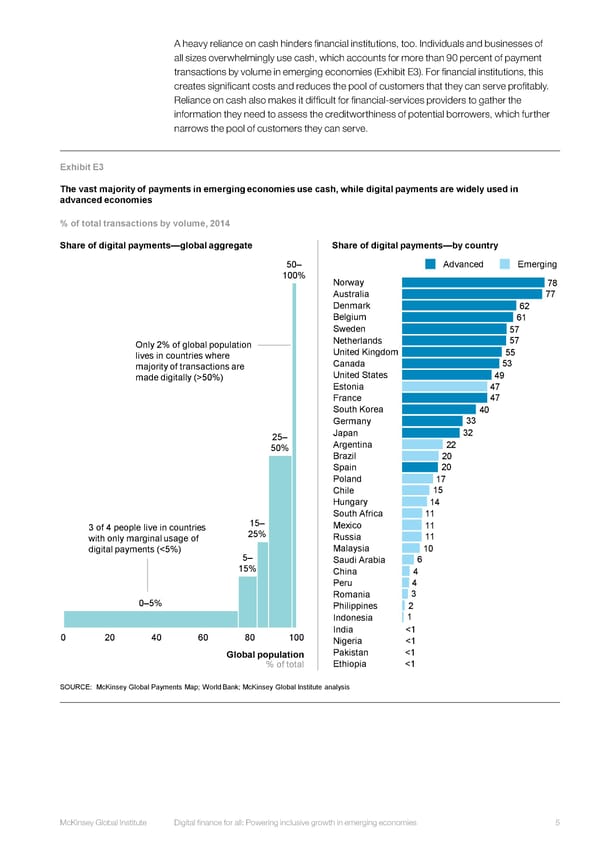
A heavy reliance on cash hinders financial institutions, too. Individuals and businesses of all sizes overwhelmingly use cash, which accounts for more than 90 percent of payment transactions by volume in emerging economies (Exhibit E3). For financial institutions, this creates significant costs and reduces the pool of customers that they can serve profitably. Reliance on cash also makes it difficult for financial-services providers to gather the information they need to assess the creditworthiness of potential borrowers, which further narrows the pool of customers they can serve. Exhibit E3 The vast majority of payments in emerging economies use cash, while digital payments are widely used in advanced economies % of total transactions by volume, 2014 Share of digital payments—global aggregate Share of digital payments—by country 50– Advanced Emerging 100% Norway 78 Australia 77 Denmark 62 Belgium 61 Sweden 57 Only 2% of global population Netherlands 57 lives in countries where United Kingdom 55 majority of transactions are Canada 53 made digitally (>50%) United States 49 Estonia 47 France 47 South Korea 40 Germany 33 25– Japan 32 50% Argentina 22 Brazil 20 Spain 20 Poland 17 Chile 15 Hungary 14 South Africa 11 3 of 4 people live in countries 15– Mexico 11 with only marginal usage of 25% Russia 11 digital payments (<5%) 5– Malaysia 10 15% Saudi Arabia 6 China 4 Peru 4 0–5% Romania 3 Philippines 2 Indonesia 1 0 20 40 60 80 100 India <1 Nigeria <1 Global population Pakistan <1 % of total Ethiopia <1 SOURCE: McKinsey Global Payments Map; World Bank; McKinsey Global Institute analysis REPEATS in report McKinsey Global Institute Digital finance for all: Powering inclusive growth in emerging economies 5
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Page 4 Page 6
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Page 4 Page 6